The use of panels to harness the power of solar energy has been around for quite a while now. And the future of this clean energy is looking bright. But to ensure that it becomes mainstream and beats electricity and non-renewable sources, we need to implement it into more households, RVs and marine transportation options too. Getting to know certain properties and the parts of the solar power systems that allow for harnessing the power of the sun is vital.
One of the more important properties of solar power systems, in this case, are charging and inverting. We all know what charging is but inverting is something less known when it comes to installing solar systems. Inverting is done by a power inverter which simply put, converts DC current to AC current. This way devices and appliances are able to use that power. You need a battery to store the power converted by the inverter but there is also a 2 in 1 solution. This device is known as an inverter charger.
Contents
What Is a Solar Inverter Charger?
An inverter charger is a device that can both convert DC current to AC to power your appliances and it also converts AC to DC to store the power in a deep-cycle battery. This type of two-way operation makes solar inverter chargers more efficient and space-saving too.
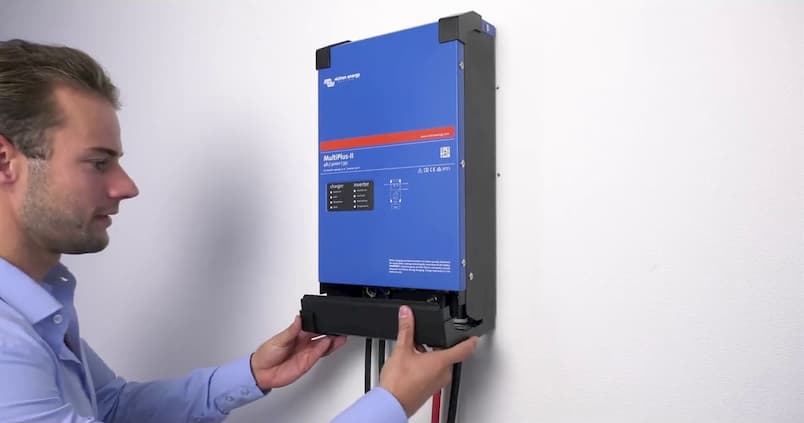

Source: suministrosdelsol.com
What to Consider When Buying a Solar Inverter Charger?
Size
An inverter charger will provide an output that small generators can produce too as well as have a decently sized battery too. The output of most inverter chargers runs between 2,000 and 4,000 watts. There are also portable ones and permanent mount inverter chargers but they are not as capable as a standalone inverter charger. Keep this in mind when shopping for a solar inverter chargers.
Battery
Since you also get a battery with this type of device, it’s important to pick one with an adequate battery capacity. Ideally, you should look for an inverter charger with a battery bank that has a capacity of at least 20% of the inverter’s size in watts. This is expressed in amp-hours, meaning a 1000 2att inverter charger should have at least 200 Ah of battery capacity. To ensure that your inverter charger has a big enough battery you’ll need to calculate electrical loads.
Read the wattage on the back of appliances and devices and multiply it by the number of hours you run each one in one day, and then divide the number by 10. This will give you the approximate number of amp-hours which the appliance/device will need to run in a 24-hour period. For example, if an inverter needs to run a 500-watt load then it will draw about 50 A of DC current. You take the 500 watts fo AC current and divide that by the efficiency of the inverter charger. Then you divide the result by 12.5 V which will give you the amps that are going to be sent through.

Source: mygenerator.com.au
Location
The best location for an inverter charger is a dark, cool and dry space which is also well-ventilated. If there are engines, fuels and other batteries nearby there is danger from explosive gasses being produced so it’s best you keep the inverter charger away from them.
Efficiency
The efficiency of an inverter charger depends on how much of the DC energy being sent to it by the panels is being converted to usable AC energy. Above-average inverter chargers are capable of converting up to 90% of the DC power they receive. Usually, the efficiency rate of inverter chargers ranges from 80% to 95%. Waveform efficiency is important especially when it comes to powering motors.
Wave Form
If you want an efficient waveform, then you should go for an inverter charger that uses pure sine waves. There is another type of waveform inverter chargers use which is known as a modified sine wave. This type of waveform is more affordable but also less efficient which doesn’t make it practical for household use. But on the other hand, it’s enough for pure sine inverters to be considered modern camping essentials.
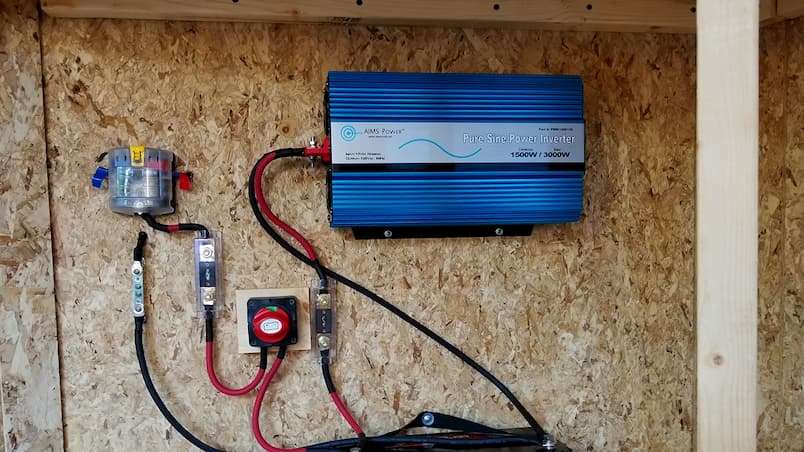
Source: rvworldstore.co.nz
Surge Capability
An inverter charger must be able to handle the surge of electricity when appliances and devices are turned on. The surge is the amount of energy needed to start a device or appliance. For example, if a 125 watt TV needs 625 watts for a couple of seconds when you turn it on make sure the inverter charger can bear that load. Without the adequate surge capabilities of the inverter charger, the TV won’t turn on. If you are using one device and need to turn it off to power on different one then that inverter charger is not of good use to you.
Interference
EMI or electromagnetic interference can be a real hindrance to an inverter charger. Usually, high-frequency inverter chargers produce a bit of EMI which can cause three major issues known as weather fax reception, SSB, and ham reception. If you choose a pure sine wave inverter charger you won’t experience any of these issues as they often meet FCC class A requirements.










